SOCIAL MEDIA
Portuguese Medical Association's Scientific Journal
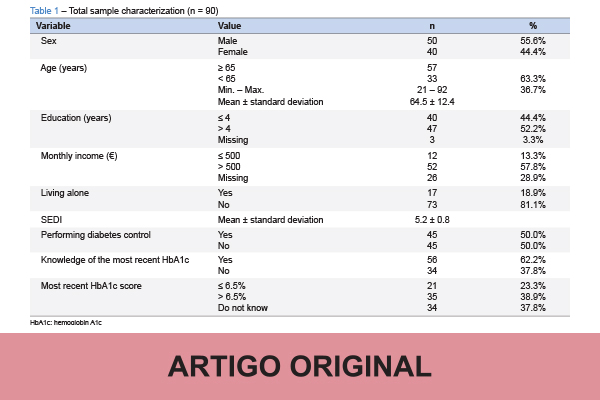
Introduction: Diabetes distress syndrome (DDS) can lead to poor outcomes and should be assessed with adapted and validated tools. One of these tools is the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) scale, which assesses diabetes distress in people suffering from diabetes (PsD). A short five-item form, PAID-5, is an easier and quicker alternative to be used in clinical and research practices, than the previous one with 20-items and has been validated by the original authors. This study intended to perform the cultural adaptation and validation of the PAID-5 scale in European Portuguese.
Methods: To create the Portuguese version of PAID-5, translation-back translation, a clinical review, and a cognitive debriefing panel were performed. A convenience sample of 90 PsD was studied in three primary healthcare units for reliability and validity tests. Reliability was studied by the internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha) and the interval coefficient correlation (ICC) under a test-retest design. Structural validity was studied by principal component analysis. The construct validity was tested by the sensitivity of the PAID-5 total score with age, most recent HbA1c test, and socioeconomic class by the Socio-Economic Deprivation Index (SEDI). Criterion validity was tested by correlating the PAID-5 total score with the psychological distress questions of the Diabetes Health Profile 18 Questions (DHP-PDQ).
Results: A Cronbach’s alpha coefficient value of 0.905 and an ICC of 0.905 were computed. In a sample of n = 90 PsD, 55.6% were males, 63.3% aged 65 years or more, SEDI was 5.2 ± 0.8 [3 to 6], 44.4% studied for less than 4 years, and 18.9% were living alone. The Spearman correlation between PAID-5 and DHP-PDQ total scores was ρ = 0.382, p < 0.001, between PAID-5 total score and age was ρ = -0.207, p = 0.050 and between PAID-5 total score and most recent HbA1c knowledge was ρ = 0.275, p = 0.040. There was no significant relationship between PAID-5 total score and SEDI ρ = 0.080, p = 0.452.
Conclusion: DDS can now be assessed in the Portuguese context, accounting for better intervention by primary care teams. PAID-5 has good psychometric properties and is a reliable scale to identify diabetes-specific distress in the Portuguese diabetic population.