SOCIAL MEDIA
Portuguese Medical Association's Scientific Journal
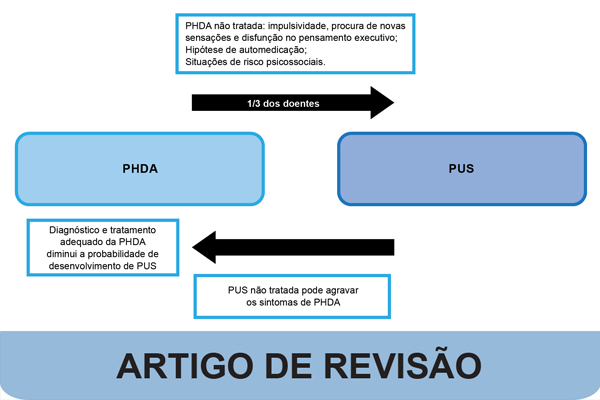
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder manifested by inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity. It is a disorder that begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood. It is associated with the emergence of various comorbidities, including, very often, the development of substance use disorders (SUD). When present simultaneously, they contribute to more severe presentations of both conditions and makes treatment more complex and challenging. Despite being different conditions, they have potentially common etiological pathways. The main aims of this article were to study the correlation between ADHD and SUD, particularly concerning the prevalence of this association, etiology and what are the best diagnostic and treatment strategies. We conclude that SUD is one of the most common comorbidities among ADHD patients, with genetic factors, neuroanatomical and neurophysiological impairments correlating both conditions. Patients with ADHD and SUD have an earlier onset of SUD, heavier abuse and worse outcomes. Special attention to this disorder is recommended in patients with ADHD. Furthermore, an active search for ADHD in patients with SUD is highly recommended, which can be carried out in the first place with self-reported scales. The appropriate treatment seems to involve a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches, with strategies targeting both conditions.